For example, if a company uses a currency forward to protect the value of an upcoming foreign sale, both the impact of the sale and the hedge would be reflected in the same reporting period. This alignment gives a clearer view of financial performance and reduces artificial swings in earnings. Hedge accounting is categorized into distinct types, each designed to address different financial risk exposures with specific accounting treatments. To qualify for hedge accounting, detailed documentation of the hedging relationship, objectives, and strategies is necessary. Net investment hedge accounting is employed to hedge the foreign currency exposure of a net investment in a foreign operation. Investment hedging may be the form of hedging that people are most familiar with.
This stability is invaluable for investor relations, internal financial planning, and maintaining favorable credit ratings. Changes in interest rates, currency fluctuations, and commodity price swings can all impact a company’s financial stability. Without hedge accounting, these risks can cause earnings to appear more volatile than the company’s actual economic position.
- Apart from this, IFRS 9 introduced a more flexible and broader range of eligible hedging instruments and hedged items.
- An accountant who carries out hedging will report a future foreign exchange transaction on the balance sheet as an asset that would be accounts receivable.
- There is no one-size-fits-all method of hedging; instead, several variations are appropriate for different types of risk.
To qualify for hedge accounting treatment, the potential changes in the cash flows must affect reported earnings; that is, they must be “highly effective” at hedging. Through hedge accounting, companies can align their risk management strategies with their overall business objectives, allowing them to protect themselves against potential market fluctuations and uncertainties. This specialized accounting approach acknowledges the potential impact of financial instruments, such as derivatives and options, in offsetting risks. It enables businesses to reflect the true economic value of risk management activities in their financial statements, providing a more accurate portrayal of their financial health and performance.
Hedge accounting helps you manage financial risks like interest rate, currency, and commodity price fluctuations by aligning derivatives with the items they hedge. Regular effectiveness testing is key to making sure the hedge works as intended, and it keeps financial reporting compliant and accurate. A cash flow hedge is designed to offset the risk of variability in expected future cash flows. These hedges are used for forecasted transactions, such as the anticipated purchase of raw materials or the expected sale of goods in a foreign currency. The accounting for a cash flow hedge differs significantly from a fair value hedge.
What Are the Different Types of Hedge Accounting?
A hedge is considered effective if it offsets at least 80% to 125% of the changes in value hedging in accounting means or cash flows attributable to the hedged risk. In summary, hedge accounting’s dual benefits of reducing income statement fluctuations and enhancing transparency help unlock key insights into corporate risk and return dynamics. When implemented properly, hedge accounting aligns financial reporting with economic reality.

Types of Hedging Relationships
In addition to documentation requirements, entities must also adhere to specific disclosure obligations related to their hedging activities. By providing transparent disclosures about their hedging activities, companies can enhance stakeholder understanding of their risk management practices and foster greater trust among investors and analysts. Physical assets, such as commodities held for production or inventory purposes, can also act as natural hedges against price fluctuations. The choice of hedging strategy depends on various factors, including the nature of the underlying exposure, market conditions, and the company’s overall risk management objectives. By employing a combination of these instruments and strategies, organisations can tailor their hedging approach to effectively manage their unique risk profiles. There must be an economic relationship between the hedged item (the asset, liability, or future cash flow with price risk exposure) and the hedging instrument (the derivative used to hedge that risk exposure).
What Are the Benefits of Hedge Accounting?
It may reduce risk exposure and smooth portfolio volatility, but can also reduce potential gains due to costs and limits. Additionally, entities must assess the effectiveness of the hedge both at inception and on an ongoing basis to ensure that it remains effective throughout its duration. Effectiveness is typically evaluated using quantitative measures that compare changes in the fair value or cash flows of the hedging instrument with those of the hedged item.
A Beginner’s Guide to Effective WhatsApp Marketing in 2024
This matching principle provides a more accurate reflection of financial performance. The effective portion of the gain or loss on the hedging derivative is initially recorded in Other Comprehensive Income (OCI), a separate component of shareholders’ equity. This amount is deferred in OCI and is only reclassified into earnings in the same period the hedged forecasted transaction affects earnings. Any ineffective portion of the hedge’s gain or loss is recognized immediately in earnings. Fair value hedge accounting If the fair value hedge meets the qualifying criteria, the hedging instrument is re-measured at fair value. The carrying amount of the hedged item is adjusted for the gain or loss attributable to the hedged risk only and is also recognised in profit or loss.
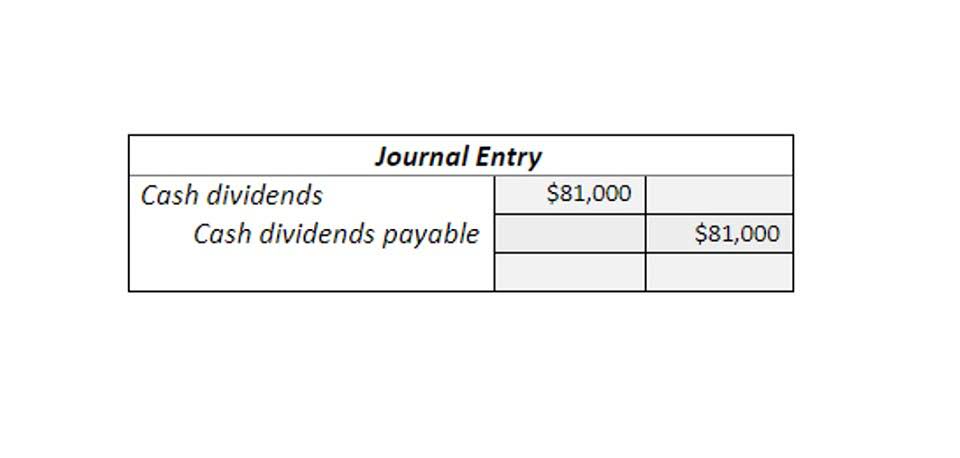
Together, these two items are examined, and a single entry is recorded for the total profit or loss. Accountants use the figures and numbers to depict the performance of the business. By placing the digits under the right category, they make it easy for everyone around to get a grip of what has been transpiring within the financial ecosystem of the company. Hedging is one such method that helps them translate the complications into easy and comprehensible financial sheets. The income statement and the balance sheet are much easily understandable once the accountants have put the pieces together.
Foreign Currency Hedge
Unlike other assets, cash retains its value during market downturns and provides immediate access to funds, offering a reliable buffer against market volatility and uncertainty. Hedge fund accounting involves the financial reporting and record-keeping of hedge funds, a sub-sector in the funds industry. It includes routine tasks such as tracking investment performance, calculating management and performance fees, reporting regulations, and using triplet call structures and highly advanced valuation models. GAAP standard for hedge accounting, shares similar principles to IFRS 9 but is more prescriptive in its approach to hedge effectiveness testing. Unlike IFRS 9, GAAP requires quantitative methods for testing the hedge’s effectiveness.
This prevents artificial volatility in the income statement and provides a more accurate reflection of a company’s financial risk management strategy. A cash flow hedge protects against variability in future cash flows, such as forecasted sales or interest payments. A company expecting to receive payment in a foreign currency might use a forward contract to lock in the exchange rate. Gains or losses from the hedge are recorded in other comprehensive income (OCI) and then reclassified into earnings when the hedged transaction effects profit or loss.
This reduces volatility in financial statements, ensuring your income statement and balance sheet accurately reflect the true economic impact of hedging activities. Fair value hedges address exposure to changes in the fair value of a recognized asset, liability, or firm commitment, due to a particular risk. For example, a company with fixed-rate debt might use an interest rate swap to convert its fixed interest payments to floating payments, hedging against changes in the debt’s fair value caused by interest rate movements. In a fair value hedge, gains and losses on both the hedging instrument and the hedged item (attributable to the hedged risk) are recognized immediately in earnings.
What is Operating Profit Ratio? Guide With Examples
- In standard accounting, gains and losses from hedging instruments such as derivatives are recorded as soon as they occur.
- Hedge accounting plays a pivotal role in effective risk management strategies for organisations operating in uncertain environments.
- Hedge accounting reflects financial performance as per the company’s risk management strategies, aligning the recognition of gains and losses with hedging activity.
This specialized accounting provides a clearer picture of a company’s risk management activities. By incorporating hedge accounting, companies can effectively manage the impact of fluctuations in the fair value of financial instruments used for hedging purposes. This is vital for aligning the financial statements with the underlying economic exposure, thereby providing a clearer representation of the entity’s risk management strategies. When foreign currency cash flows change due to the foreign exchange rate changing, cash flow hedges can reduce the impact.
IFRS 9, Financial Instruments.
The income statement information can be transferred to the balance sheet for further analysis. If this process is changed, the financial reports of the company will change. An accountant who carries out hedging will report a future foreign exchange transaction on the balance sheet as an asset that would be accounts receivable.
Learn about emerging trends and how staffing agencies can help you secure top accounting jobs of the future. Having learned about this, it is important to highlight that this process opens up channels for fraud. It does so by compensating for changes that are not reflective of an investment’s performance.